UV radiation and skin cancer

Types of UV radiation
- UVA makes up most of the UV that reached the earth surface. It reaches the deeper layer of the skin causing skin ageing, eye damage and skin cancer.
- UVB is mostly absorbed by the Ozone layer and other substances before it reaches the earth’s surface. It causes sunburn and is the major cause of skin cancer.
- UVC is mostly filtered before it reaches the earth by the Ozone layer and other substances. Problems can arise if the Ozone layer is thin, such as is the case over Australia. Some UVC can then reach the earth surface and increase the risk of those exposed to it to skin cancer.
Some myths about UV rays
- Myth 1: You can see and feel UV rays.
Completely false! There are rays from the sun that can be seen (sunlight) and felt (infrared) but UV rays cannot be seen or felt. - Myth 2: You are only exposed to UV rays when the sky is clear and you can see the sun.
Again, not true! Up to 90% of UV rays can get through light clouds so even on cloudy Irish days you need to protect your skin for UV damage. - Myth 3: In Ireland we don’t have enough good weather to cause a problem with UV rays.
Don't believe a word of it! With the amount of cloudy days we have many people seem to think that UV rays are not something we need to worry about when out and about in Ireland. This is untrue. Skin cancer is our most common cancer and most cases are caused by UV rays. Even in Ireland we need to take care when outdoors, especially from April to September, by following the SunSmart code.
What affects the amount of UV rays you are exposed to?
While UV radiation is present all year round many factors influence how much you are exposed to. They include:
- The time of day: UV rays are stronger in Ireland from 11 am to 3 pm.
- The time of year: UV rays reach the earth all year round but in Ireland exposure is usually greatest from April to September.
- Altitude: The higher up you go the higher the level of UV radiation. For this reason take extra care if you are hill walking.
- Cloud cover: Cloud cover generally reduces the amount of UV rays you are exposed to. However up to 90% of UV rays can pass through light clouds so even on an overcast day UV levels can be high enough to damage your skin.
- Where you are in the world: The closer you move to the equator the higher the UV level.
- Reflective surfaces: UV rays can be reflected back from some surfaces making your exposure greater. Concrete, for example, can reflect 10% of UV rays. Dry sand can reflect up to 15%, sea foam about 25% and snow 80%!
- Ozone layer: Some of the UV rays that would otherwise reach the earth are blocked by the ozone layer. Take extra care in areas where the ozone layer is depleted - in Australia, for example.
How can UV rays affect your health?
Being exposed to too much UV radiation causes sunburn, tanned skin, skin ageing, premature wrinkles and eye damage.
Sunburn
The amount of UV exposure needed for skin to burn is different from person to person. It depends on your skin type. If you have very fair skin you will burn more quickly than those with darker skin.
Getting sunburnt at any age is a sign that the DNA in your cells has been damaged by UV rays. This damage can lead to skin cancer later in life, in particular melanoma skin cancer.
Tanned skin
You may think that having a tan is healthy but there is nothing healthy about a tan caused by UV radiation. It is a sign that your skin has been damaged and is trying to protect itself from further UV damage. While much of this damage will be repaired, some of it remains and builds up over the years with every tan or sunburn you get. It is this built-up damage that can lead to skin cancer later in life.
Eye damage
UV rays can damage the eyes and lead to a number of problems including:
- Mild irritation of the eye
- Worsening conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eye)
- Increased risk of cataracts which can lead to difficulties with sight
- The development of spots that could result in blindness
- Cataracts
- Eye cancer in later life
Ageing and premature wrinkling
UV rays can reach the deeper layers of the skin and cause it to wrinkle and sag. It also dries out the skin making it leathery and coarse.
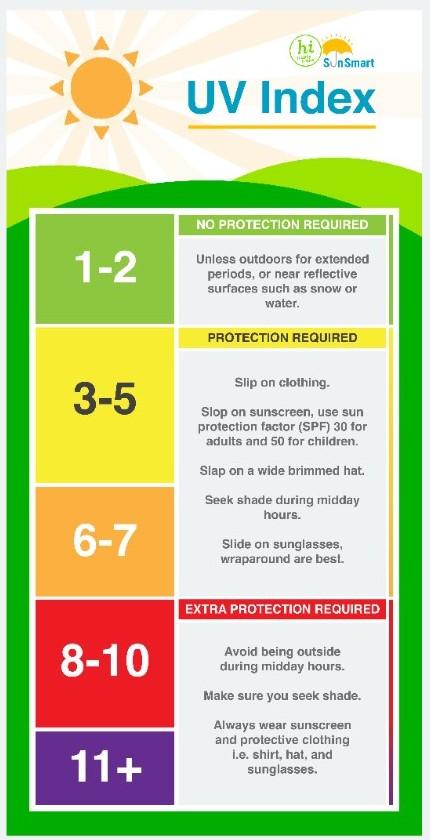
The UV Index
The UV Index tells us the level of UV radiation that is expected at the earth’s surface. It is a scale that runs from zero upwards. The higher the level the less time it takes the skin to burn and the greater the risk of skin damage which can lead to skin cancer.
Know the UV index
If the UV Index is 3 or more it is important to follow the SunSmart code.
The Irish Cancer Society advises that when in Ireland we follow the SunSmart code from April to September to protect our skin, but if the UV Index is 3 or more make sure to take extra care.
Stay safe by limiting time in the sun when UV is strongest. Check the UV index on the Met Eireann website

If you are concerned about skin cancer or have any questions at all, speak to a cancer nurse by visiting one of our Daffodil Centres or by contacting a cancer nurse on Freephone 1800 200 700 or by email supportline@irishcancer.ie
For more information
Phone
1800 200 700



