What are the types of non-melanoma skin cancer?

Basal cell cancer (BCC)
BCC affects the cells at the base of the outer layer of your skin, the epidermis. It is the most common type of skin cancer.
Most basal cell cancers are slow growing and develop over months and years. If left untreated, they can grow bigger and form an ulcer known as a rodent ulcer. Usually basal cell cancers do not spread to other tissues and organs.

Squamous cell cancer (SCC)
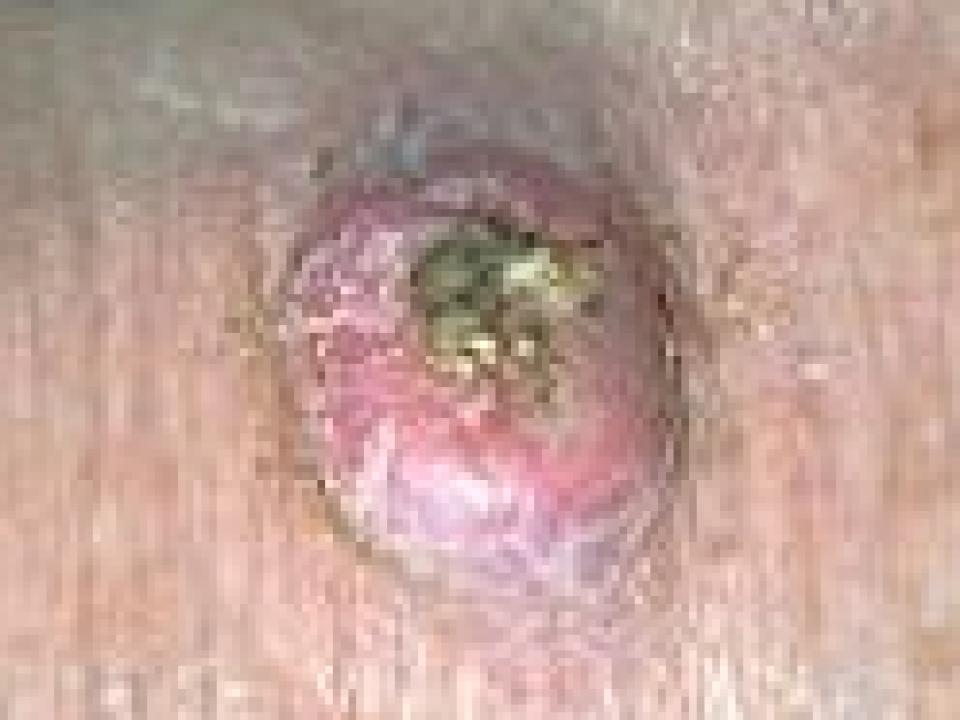
SCC affects the squamous cells, which are the cells nearest the surface of your skin. They lie just above the basal cells. It is the second most common type of skin cancer in Ireland. If left untreated, squamous cell cancer can grow bigger or spread to other parts of your body. Even so, most patients are completely cured with just surgery.
Other skin conditions
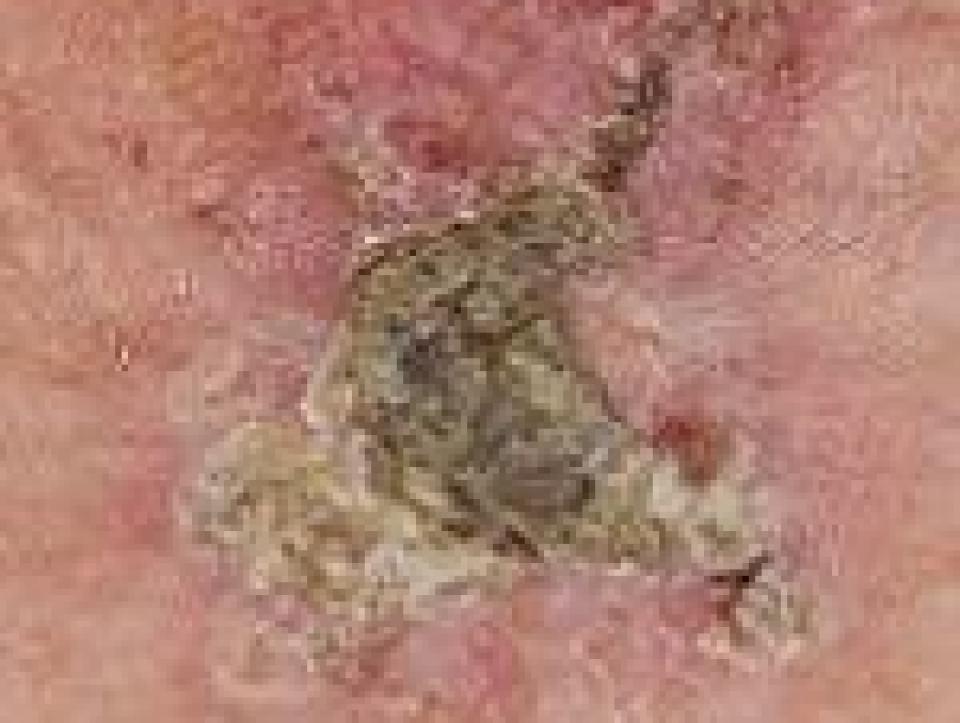
- Actinic keratosis: Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that can sometimes turn into a squamous cell carcinoma. Sun damage may cause rough scaly spots or patches on the skin called actinic keratoses. These may be pink-red or flesh coloured. They can appear on the face, ears, back of hands and arms of middle-aged or older people with fair skin. This kind of skin damage is caused by the casual exposure to sunlight over the years, from living in sunny climates or working outdoors. Actinic keratoses can also be called solar keratoses.
- Bowen’s disease: Bowen’s disease is a skin growth found only on the outer layer of the skin. It looks like scaly red patches that may be crusted. It is also known as ‘squamous cell carcinoma in situ’ because it remains in the outer skin layer only and does not grow deeper into the skin. The biggest risk factor for Bowen’s disease is long-term exposure to the sun. It can also occur in areas that have had no exposure to the sun. Women are usually affected more than men.
Less common non-melanoma skin cancers
These are rare and more serious types of non-melanoma skin cancer:
- Kaposi sarcoma: This skin cancer develops in the skin’s blood vessels and causes red or purple patches on the skin or mucous membranes. It affects people with weak immune systems, such as those with AIDS or those taking medications that affect their immune system.
- Merkel cell cancer: This cancer forms firm, shiny lumps on or just beneath the skin. These may be red, pink or blue in colour. Merkel cell cancer is usually found on the head, neck, arms and legs.
- Lymphoma of the skin: This is caused by the uncontrolled growth of a type of white blood cell within the skin called a T-cell, or occasionally a B-cell.
For more information
Phone
1800 200 700