Brain tumours
A brain tumour is a mass (lump) formed by an abnormal growth of cells in the brain.
A primary brain tumour is a tumour that starts in the brain. About 400 people are diagnosed with primary brain tumours each year in Ireland. Men are more likely than women to develop a brain tumour.*
Signs and symptoms
Learn about the signs and symptoms of brain tumours. You are more likely to survive cancer if you find it at an earlier stage.
Treatments
There are a number of different treatments available for brain tumours. Your medical team will explain the best treatment options for you.
What is a brain tumour?
A brain tumour is a mass (lump) formed by an abnormal growth of cells in the brain.
Brain tumours can cause problems if they press on the brain or grow into the brain tissue.
Not all brain tumours are cancerous (malignant). Grades 1 and 2 are benign (not cancerous) – although they can come back and become malignant.
Symptoms will depend on which area of the brain is affected by the tumour, as different areas of the brain control different activities.
There are many different types of brain tumour, depending on which cells are affected. Read more about types of brain tumour.
Primary brain tumours develop either from cells inside the brain or from cells that make up the covering layers of the brain. Primary brain tumours usually do not spread to other parts of the body. In this section, we are talking about primary brain tumours.
Secondary brain tumours spread to the brain from cancer cells in other parts of the body such as breast cancer cells or lung cancer cells.
Brain and spinal cord tumours in children
If you want information on brain tumours in children, please see our booklet:
What are the types of brain tumours?
Brain tumours can be described as gliomas (glial brain tumours) or non-glial brain tumours.
Read more about gliomas and non-glial brain tumours
What is the brain?
The brain is made of countless nerve cells. It is the control centre of your body.
Each area of the brain controls different activities. This means that a tumour can affect different activities and give different symptoms depending on where it is found in the brain. There are 3 main parts of the brain: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.
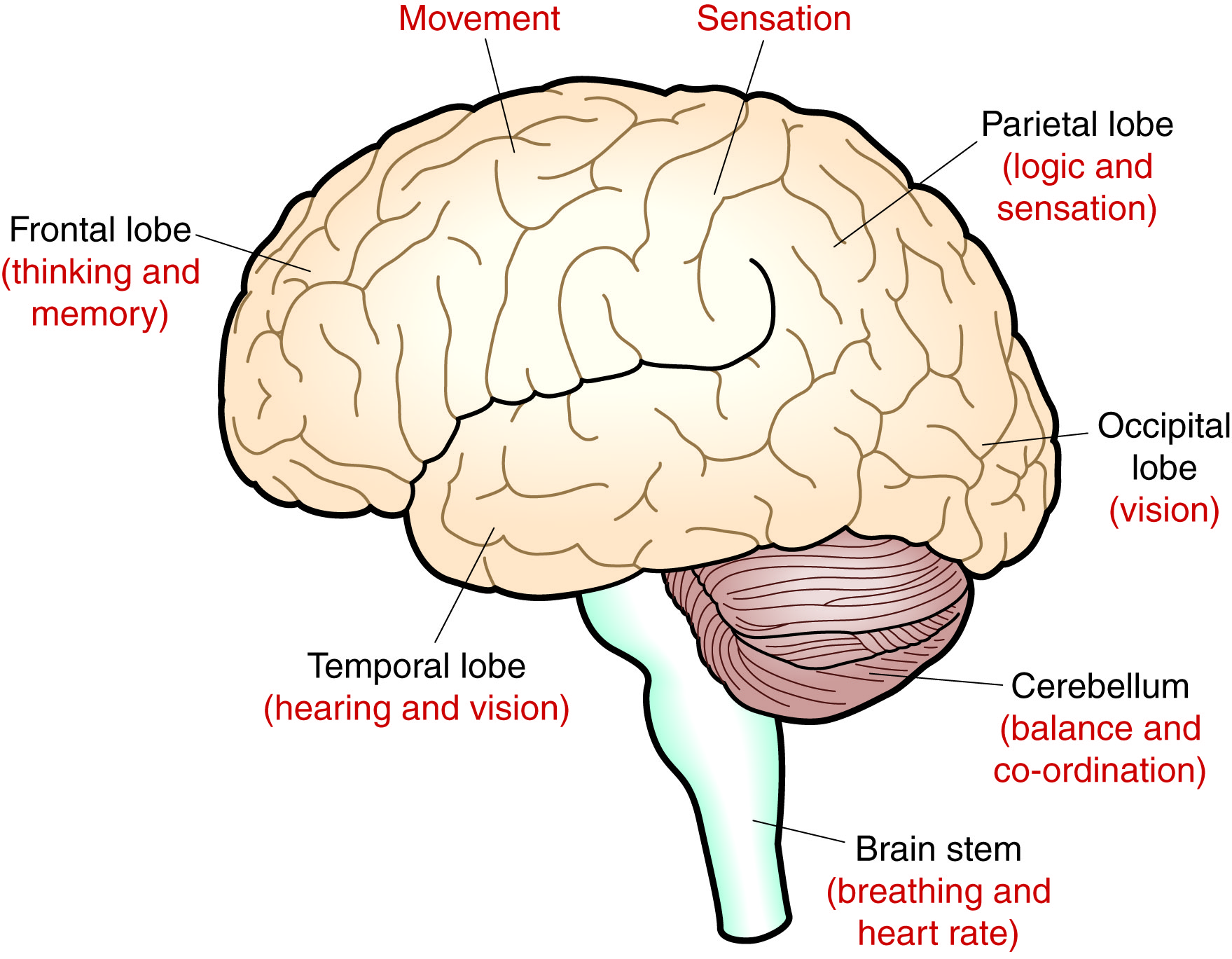
The cerebrum is the largest area of the brain. It controls thinking, memory, behaviour and personality.
The cerebellum is the back part of the brain. It helps with balance and coordination.
The brainstem is located at the bottom of the brain and attaches the cerebrum to the spinal cord. It is here that our basic bodily functions are controlled, including breathing, heartbeat and blood pressure and reflexes.
The brain is wrapped in three thin membranes called meninges.
A watery fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fills the spaces between the meninges and cushions the brain. The brain is protected by the bones that form the skull.
What increases my risk of brain tumours?
There are certain things called risk factors that can increase your chance of getting a brain tumour. These include:
Primary brain tumours can occur at any age but they are more common in people between the ages of 50 and 70. Certain types of brain tumour are more common in young adults and children.
Men are more likely than women to develop most types of brain tumours.
There are certain rare genetic conditions that have been linked to an increased risk of brain tumours. These include neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2, tuberous sclerosis, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, Turcot syndrome and Gorlin syndrome. If you have these conditions it does not mean you will develop a brain tumour. But you have a slightly higher risk than someone without these conditions. However, if anyone in your family is worried about having a genetic risk linked to brain tumours, they should discuss it with their doctor.
Children, teenagers or young adults who have been exposed to radiotherapy in the past have an increased risk of developing a tumour at the treatment site.
If your immune system is weak as a result of a HIV infection or long-term treatment with immunosuppressants, you may be at greater risk of developing a rare type of tumour called primary (cerebral) lymphoma.
Unproven causes
Many people are concerned that mobile phones, power lines and some viruses can cause brain tumours. Research has found that there is no clear link between these and brain tumours.
There is also no evidence to show that hurting your head in an accident can cause a brain tumour.
Remember, having a risk factor does not mean you will get a brain tumour.
Medical content updated from our 'Understanding primary brain tumours' booklet (2023). Reviewed by Mr Stephen MacNally, Consultant Neurosurgeon and Neuro Oncology Lead and Eloise Cowie, Clinical Nurse Manager 3, Neuro Oncology.
Talk to a Cancer Nurse

Support Line
Our Daffodil Centres

*The Irish Cancer Society uses the most up-to-date cancer statistics from the National Cancer Registry Ireland, available on www.ncri.ie

