What increases my risk of melanoma?

On this page:
Everyone is at some risk for melanoma, but increased risk depends on:
- Exposure to UV light: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun’s rays (even on cool or cloudy days) or tanning lamps and sunbeds increases the risk of melanoma.
- Sunbeds: People who have used a sunbed had a 20% increased risk of melanoma. Starting to use them young increases the risk even more.
- Skin type and eye colouring: People with fair skin with fair or red hair and blue, green or grey eyes are more at risk.
- Moles: Having a large number of moles or moles which look unusual.
- Age: Risk of developing melanoma increases with age.
- Family history of melanoma or skin cancer: Your risk increases if you have a family member with skin cancer. Remember though: Melanoma is not infectious and cannot be passed on to others.
- Weakened immune system: For example, after an organ transplant, when taking medicines that suppress your immune system or with illnesses such as HIV/AIDs.
- Genetic skin disorders: Your risk is greater if you have a genetic condition that makes your skin more sensitive to sunlight, such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Having a risk factor doesn’t mean you will get cancer. Sometimes people with no risk factors get the disease. If you’re worried, talk to your GP or talk to one of our cancer nurses. Call our Support Line on 1800 200 700 or visit a Daffodil Centre.
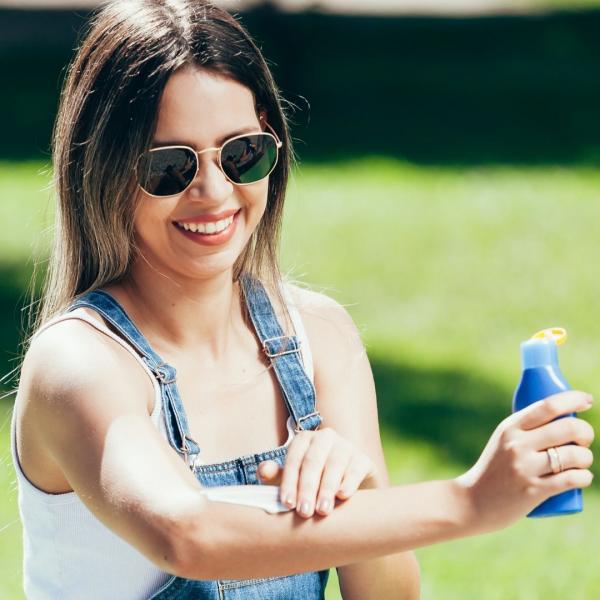

Reducing your risk of melanoma
The most important things you can do to reduce your risk of melanoma are:
- Protect your skin from UV rays from the sun.
- Don’t use sunbeds.
- Check your skin regularly for any unusual changes.
Read more about these and other cancer risk-reduction tips.
For more information
Phone
1800 200 700