Neutropenia (low white blood counts)

What is it?
Neutropenia is when the level of neutrophil white blood cells are low. When the neutrophil levels are low, you are more at risk of infection, because white blood cells help the body fight infection.
What are the symptoms of neutropenia?
Neutropenia itself may not cause symptoms. Your doctor may find out you have neutropenia when your blood cell levels are tested. Or you may get symptoms of infection if neutropenia is affecting your ability to fight off infections.
Symptom of infection include:
- High temperature 100.4°F (38°C) or a very low temperature 35°C (95°F)
- Feeling shivery or unwell
- A new or worsening cough
- Shortness of breath
- Vomiting or diarrhoea
Always contact the hospital if you have a high temperature or other symptoms of infection.
How is neutropenia treated?
A low level of neutrophils can be improved by injecting growth factors to stimulate the bone marrow to produce more white blood cells. For example, G-CSF.
Not all patients are suitable for growth factors, as only a small number will respond to them. Your doctor will advise you about this.
You will also be advised to avoid infections. Read tips on how to cope with an increased risk of infection.
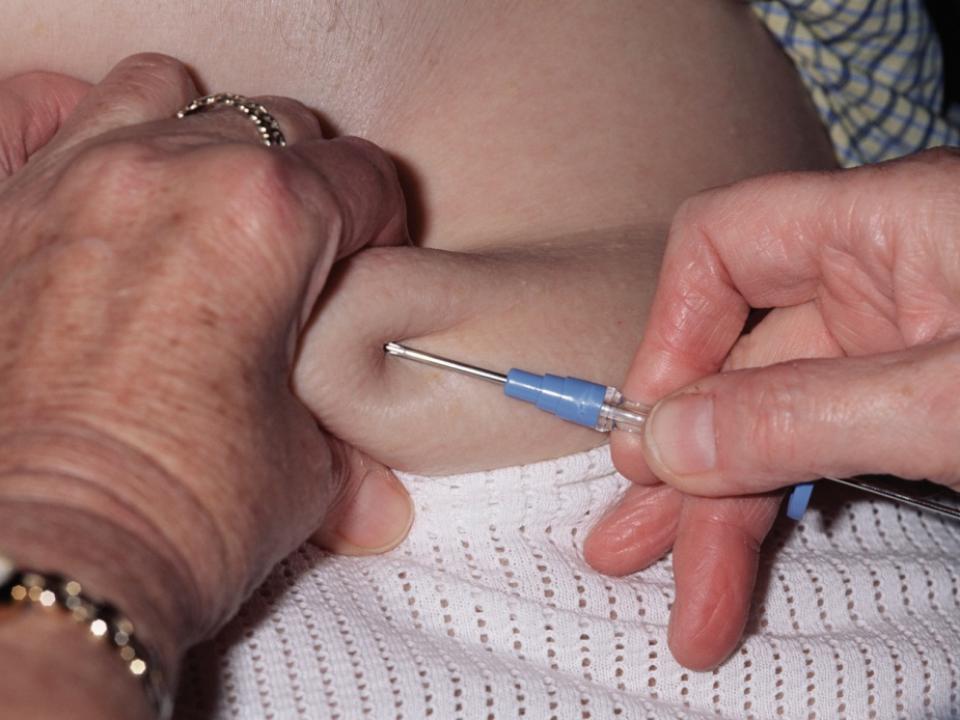
Giving growth factors
Growth factors are usually given as injections under your skin.
Your nurse can discuss who will give these injections when you are at home. You may choose to give the injection yourself, or a relative, GP or public health nurse can do it instead. Side-effects are usually quite mild. If you are receiving G-CSF to increase your white blood cells, you may get aching in your bones and muscles. This aching can usually be relieved by taking a mild painkiller. But do let your nurse or doctor know as they can prescribe the best medication for you. There are some possible serious side-effects but they are rare.
For more information
Phone
1800 200 700



