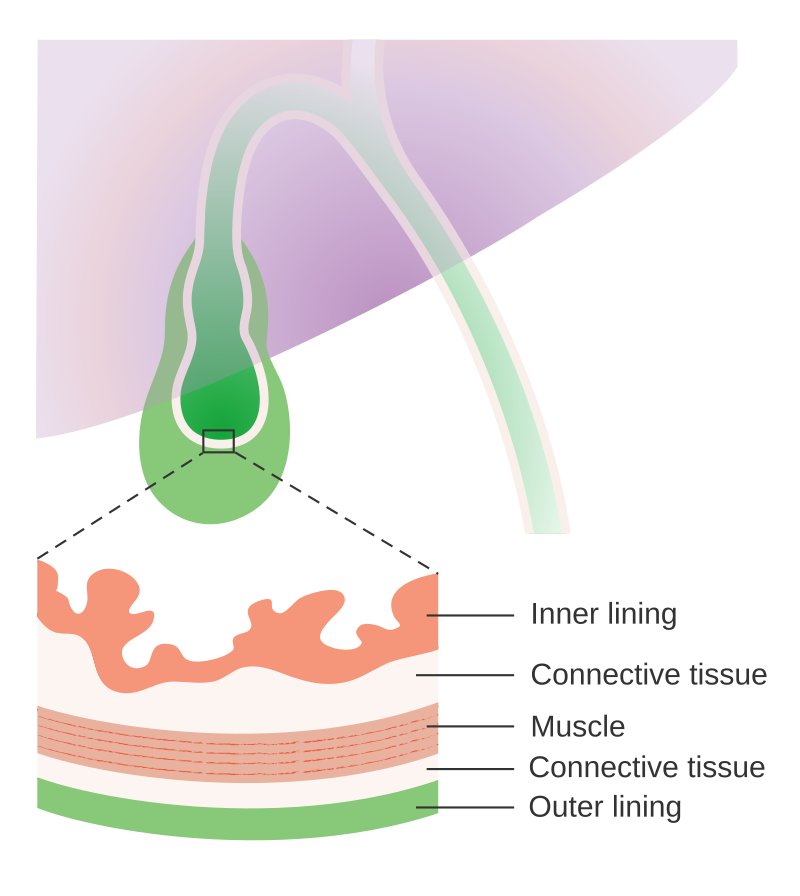
Grading describes how cancer cells look under a microscope compared with normal cells. This will give your doctors an idea of how the cancer may grow and whether it is likely to spread. Knowing the grade helps doctors to plan your treatment.
Gallbladder cancer is graded from grade 1-3. Higher grades look more different to normal cells and tend to grow more quickly.