Ascites
Ascites (“ah-site-ease”) is a build-up of fluid in the abdomen (tummy area), which can cause symptoms such as pain.
What causes ascites?
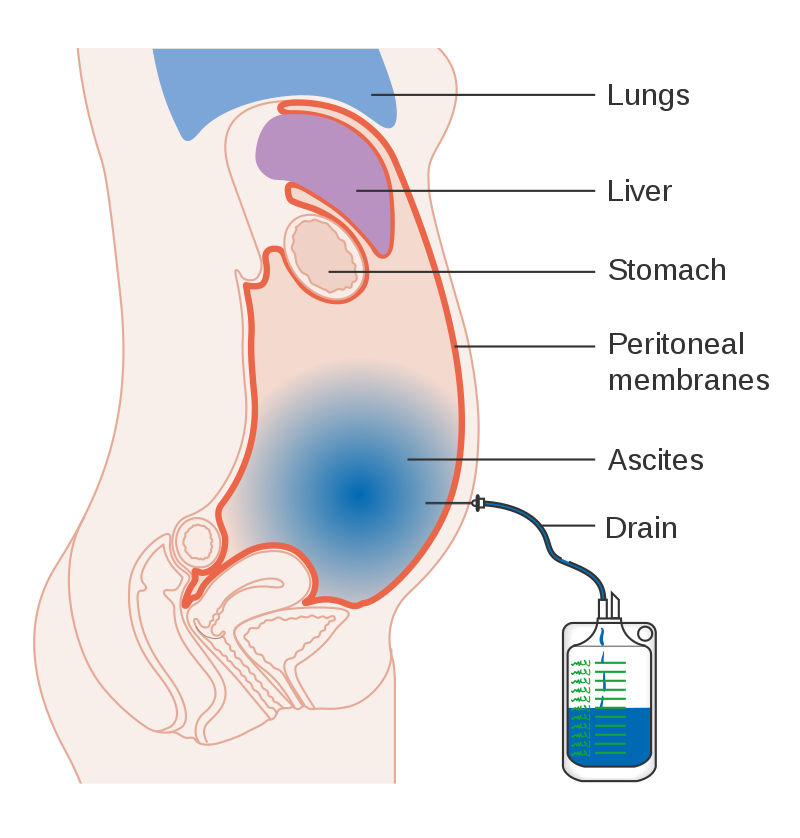
Ascites is when the fluid between the organs in your stomach and the wall of your abdomen (tummy) builds up. The fluid is contained between 2 layers of tissue.
The fluid can build up over a few weeks or more suddenly – in a few days. This can be caused by:
- Cancer cells in the lining of the tummy causing fluid to build up.
- Cancer cells blocking the lymphatic system - which normally removes excess fluid from the body - causing fluid to build up.
What are the symptoms of ascites?
- Tummy feeling tight or clothes feeling tighter
- Bloating – for example, your tummy may look like you are pregnant
- Pain in your tummy or back
- Reduced appetite
- Indigestion
- Constipation
- Needing to pee often
- Feeling breathless
- Feeling tired or weak
What should I do if I have ascites symptoms?
Tell your doctor if you have symptoms of ascites. They can do tests to find out the cause – for example, an ultrasound scan, blood test or taking a sample of fluid from your tummy using a needle.
How is ascites treated?
The doctor can remove the fluid with a long, hollow needle attached to a tube called a drain. You will have a local anaesthetic, so you shouldn’t feel any pain. The fluid will drain through the tube over a few hours or days, depending on the amount of fluid.
You may have to have another drain if the fluid comes back again. If the fluid keeps coming back, your doctor may suggest a catheter (a flexible tube). This can be left in place to drain off the excess fluid, your medical team will show you how to look after this tube when at home and discuss any care that is needed. You may also be given tablets (diuretics) to slow down the build-up of fluid.



Talk to a Cancer Nurse

Support Line
Our Daffodil Centres


