Types of breast reconstruction
There are different types of breast reconstruction. Your medical team will advise you on what will work best for you.
Implant-only reconstruction
This type of reconstruction uses an artificial breast implant. It is usually the simplest type of reconstruction.
It may be suitable if you are having immediate breast reconstruction or if you are having bilateral reconstruction (reconstruction of your 2 breasts). There are two main types of implant reconstruction:
If your breast is reconstructed using an implant on its own, a silicone prosthesis can be placed under the skin and muscle of your chest. This replaces the missing breast tissue removed at the time of your mastectomy.
It is more suitable for immediate reconstruction and if you have smaller breasts. It can be used if the type of mastectomy you had did not take all the skin away (a skin-sparing mastectomy).
The implant is like a balloon with an outer shell of silicone and a valve or port to allow saline (salt water) to be injected into it. It is placed beneath the muscle of your chest wall during an operation.
When your wound has fully healed, your surgeon will inflate the implant every 2 to 3 weeks in the outpatient clinic. This allows your skin and muscle to gradually stretch until you are happy with the size.
Usually another operation is needed to remove the expander, which is replaced with a permanent implant.
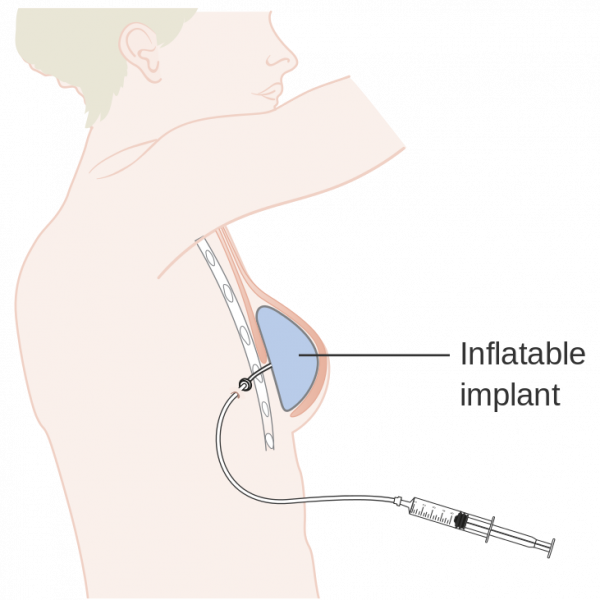
Image of expander implant. Source: CRUK, Wikimedia Commons
Reasons for choosing implant surgery
- You prefer it
- You have no spare body tissue to use for flap surgery
- Your health may not allow for a bigger operation
- You can recover quickly from this kind of surgery
- You do not want a bigger operation involving scarring elsewhere on your body
Reconstruction using a flap of your own tissues
Flaps can use muscle, fat and skin or just fat and skin taken elsewhere in your body to reconstruct your breast. The areas where the tissue is taken from can vary. For example:
- Flap from your back – with or without an implant (latissimus dorsi (LD) flap)
- Flaps taken from your tummy area (tray flap)
- Flaps taken from other areas, such as your buttocks or upper inner thigh
- Reconstruction using skin and fat (and no muscle) from your abdomen (DIEP flap)
Flap surgeries have the advantage of giving a more natural-looking result.
Read more about the different types of flap surgery.
Lipofilling and creating a new nipple
As well as implant or flap surgery, you may have other procedures to give the best, most natural result.
Fat is removed from another part of your body and transferred to your breast area to fill out a dent, improve the shape or increase your breast size. It generally works best when some time has passed after breast reconstruction, once healing has taken place, and any swelling reduced.
It involves :
- Fat is taken by liposuction from an area where there is extra tissue, such as your hips or tummy.
- It is specially treated in theatre on the day of surgery.
- It is then injected to either increase the size or shape of a previous reconstruction or correct a defect in the curve of your breast or chest.
- Lipofilling is usually done under local anaesthetic, but a general anaesthetic can be used depending on the size of the area to be treated.
- Lipofilling may need to be repeated if the first treatment does not fully correct the dip in shape.
Usually with a mastectomy, your nipple is removed along with your whole breast. The final stage in being satisfied with your new breast is often having your nipple reconstructed.
- Creating a nipple shape: The most common way to do this is to make flaps of tissue. These are sewn together on the breast to make a nipple shape. A nipple can also be made by taking a graft from another part of your body, or from your other nipple areola.
- Applying colour to the nipple: At a later stage, usually some weeks after the nipple shape has been made, your areola will be filled in using colour. Normally, a medical tattoo is used to apply a colour that matches your natural areola.
For a few days afterwards, your new nipple may be sore and uncomfortable. A scab usually forms that will come off after a few days. You can cover the area with a dressing as some oozing or weeping may occur.
You might need more than one session to get your best colour result. You might also need top-ups of the colour after 18 months to 2 years. This is because the pigment is semi-permanent and the colour can fade over time.
Talk to a Cancer Nurse

Support Line
Our Daffodil Centres


